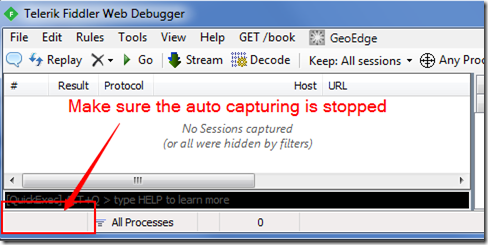
Fiddler is a very handy tool for http related debug. After starting, it automatically start to capture any http request go through system proxy. Also it by default listen to port 8888. For debug Java application, we stop the automatic capturing, only use the port 8888.

This articlae is for debug HTTPS request from java application, if the java application send out HTTP request, please go to this article.
Target
You have a java application, which send https requestion out. For debugging purpose, You want to find out what exactly be sent out as well as its response.

Solution
Different from http, proxy https request need more steps.
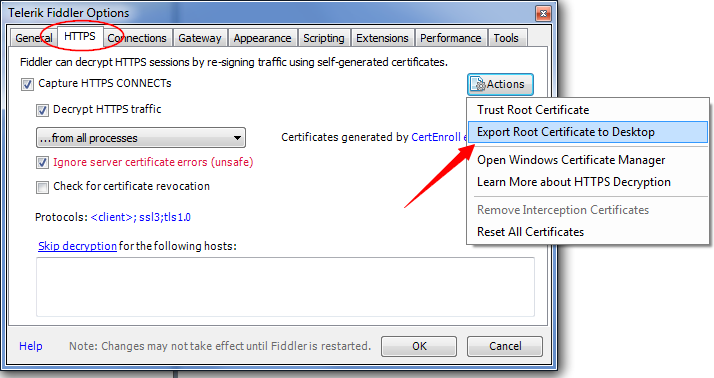
1. Get Fiddler Root Ceretificate file ( .cer file)
Open Fiddler, tools->Telerik Fiddler options

Choose HTTPS tab-> Export Root Certificate to Desktop.
Now you should be able to find the Certificate file “FiddlerRoot.cer” on desktop. Let’s copy this file to directory C:/keystore.

2. Create truststore file from Fiddler Root Certificate (.cer file –> .jks file)
Use keytool to generate keystore file.
keytool -importcert -alias fiddler -file c:\keystore\FiddlerRoot.cer -keystore c:\keystore\fiddler_keystore.jks -storepass abcd1234

Now we have the fidder_keystore.jks file. From command line you can also find the storepass was set to “abcd1234”
3. Set proxy for JVM
Set http proxy for JVM either from java command or inside java code, here is a simple example by setting System properties in Java code.
package com.shengwang.demo;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
public class DemoMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
enableHttpsProxy();
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String text = restTemplate.getForObject("https://www.facebook.com/", String.class);
System.out.println(text);
}
private static void enableHttpsProxy() {
System.setProperty("https.proxyHost", "127.0.0.1");
System.setProperty("https.proxyPort", "8888");
}
}
At the beginning of the code, we set proxy for https for JVM, then we try to access facebook by https.
4. Use the truststore file when running your Java application
If directly run the previous DemoMain class, you will get a Exception during the SSL handshaking, complain unable to find a validate certificate. So we need to run the DemoMain class with following JVM options:
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=c:/keystore/fiddler_keystore.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=abcd1234
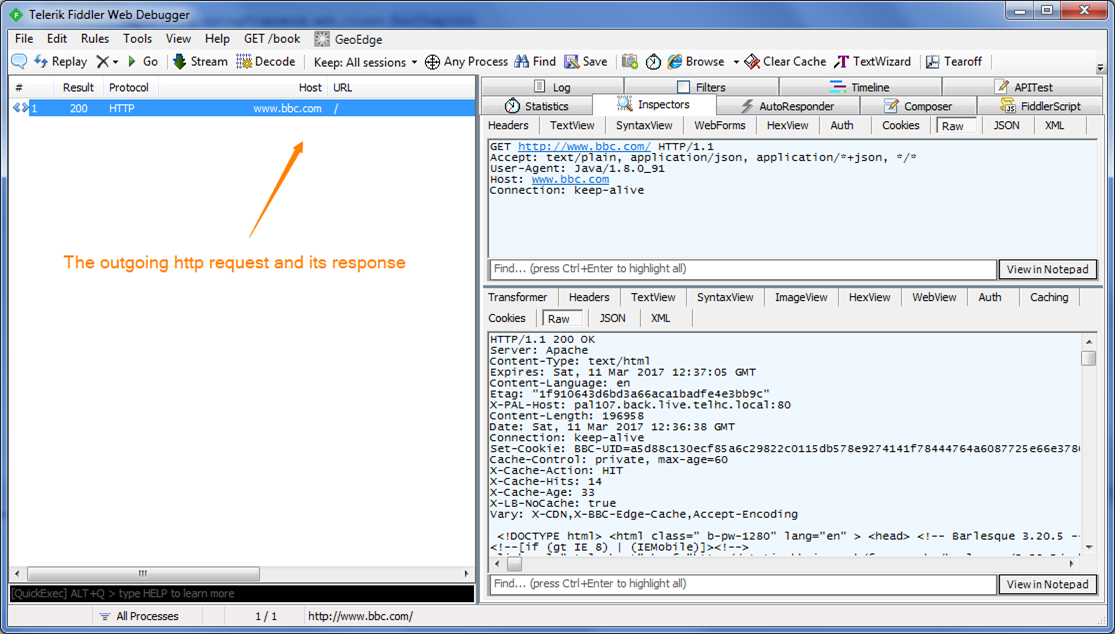
These 2 options tell JVM where to find the keystore file and the corresponding password to use the keystore. After you run the DemoMain with above options, we should be able to see the https request and its response from fiddler UI. Both request and response are decoded, so it’s very helpful during development.