It’s a frequently encountered pitfall when using hibernate, also has entity with properties type defined as java.util.Date.
In short, although the entity’s property is defined as java.util.Date in entity class, but at runtime hibernate will never set it as java.util.Date, but java.sql.Timestamp!
Since java.util.Date is the parent class of java.sql.Timestamp, so in your code whenever treat this field as java.util.Date, there is no exeption at compilation or runtime. But the unexpected result often come when the eqals operation involved.
An instance of java.sql.Timestamp will NEVER equal to any instance of java.util.Date! (caused by Timestampl’s impl of equals method, see javadoc of Timestamp), even logically they represent the exactly time.
The following example shows you how this pitfall looks like.
Entity class
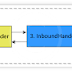
Suppose we have a entity class ‘User’.
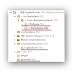
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
@Id
private Long id;
private String name;
@Column(name = "changed_at")
private Date changedAt;
// setter getter omitted
}There is a field “changedAt” defined as time java.util.Date.
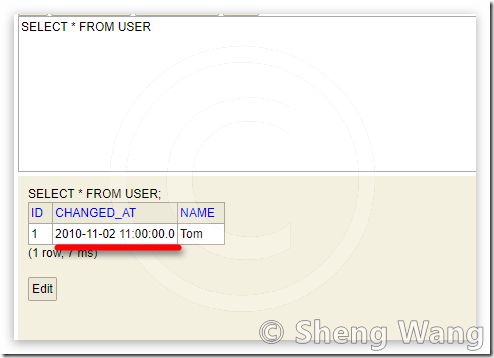
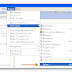
Database
In database, we have following data
code to show the pitfall
Let’s run the following code.
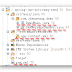
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date a = df.parse("2010-11-02 11:00:00"); // a is instance of Date
Date b = userRepository.findById(id).get().getChangedAt(); // b is actually a instance of Timestamp
System.out.println("a.getTime() == b.getTime() is " + (a.getTime() == b.getTime()));
System.out.println("a.equals(b) is " + a.equals(b));
System.out.println("b.equals(a) is " + b.equals(a));Although the variable is also defined a ‘Date’ but thanks to hibernate, at runtime it’s an instance of Timestamp
Then we have the following output
a.getTime() == b.getTime() is true a.equals(b) is true b.equals(a) is false
As you can see, even a and b represent the same logic time, the equals result are different. You many wonder why b.equals (a) is false, here is the reason.
public boolean equals(java.lang.Object ts) {
if (ts instanceof Timestamp) {
return this.equals((Timestamp)ts);
} else {
return false;
}
}Above is the equals() impl of class java.sql.Timestamp. Caused by the instanceof check, a instance of Timestamp never equals to instance of Date.
Conclusion
- When work with hibernate and entity with date, always remember they are not real ‘Date’, but ‘Timestamp’,
- Always use Data instance’s equals() methods